ALS Compendium
Title: Establishing a novel C. elegans model to investigate the role of autophagy in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Year Published: 2013
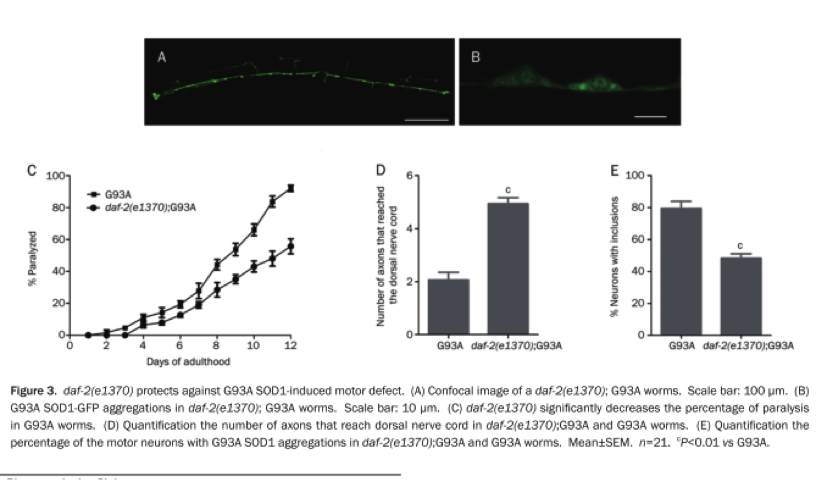
Observation: Expression of G93A SOD1 in motor neurons caused age-dependent motor defects accompanied by significant SOD1 aggregation and axon guidance failure. After 12 d, over 80% of the G93A worms became paralyzed, whereas less than 10% of the controls showed a paralytic phenotype. Crossing the daf-2(e1370) mutation into the G93A SOD1 mutant worms significantly ameliorated the motor defects, SOD1 aggregation, and axon guidance failure.
Comment: G93A SOD1 expression in motor neurons of C. elegans results in characteristic alterations of ALS. Increased autophagy protects C. elegans motor neurons against the toxicity of mutant SOD1.
Citation: Li, J., Huang, K., & Le, W. (2013). Establishing a novel C. elegans model to investigate the role of autophagy in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 34(5), 644–50. doi:10.1038/aps.2012.190
Back to Homepage