ALS Compendium
Title: Differential expression of c-Ret in motor neurons versus non-neuronal cells is linked to the pathogenesis of ALS
Year Published: 2011
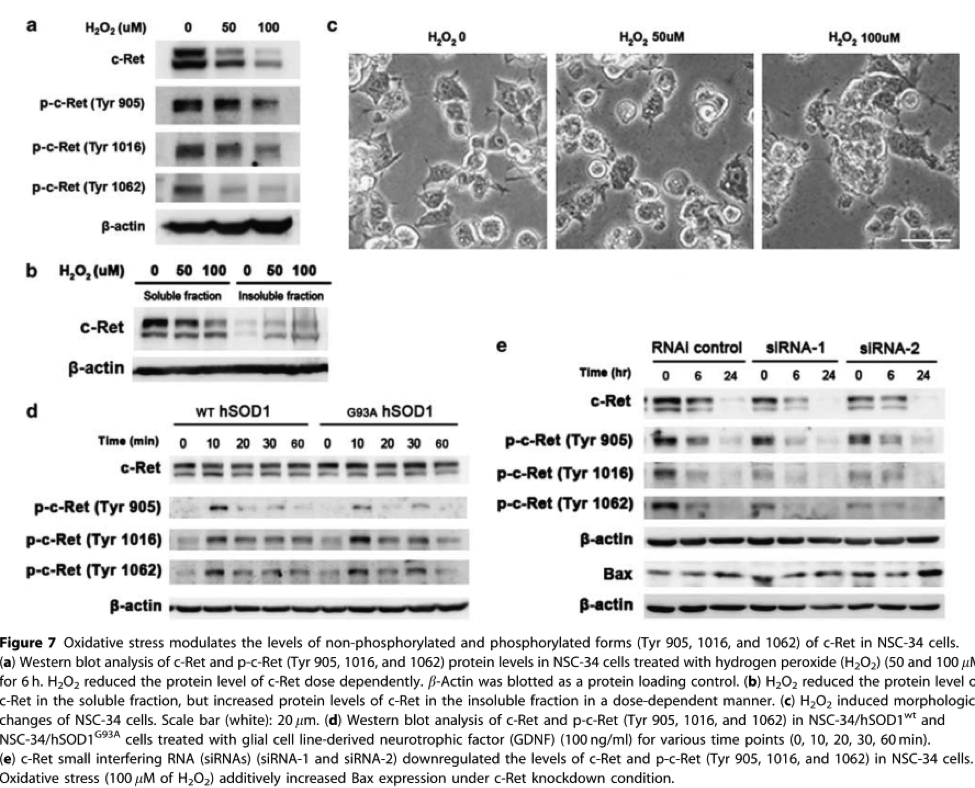
Observation: Levels of cRet is altered in spinal cord of humans and ALS mice. Oxidative stress modulates the level of cRet and pcRet and GDNF dependent cRet signaling is altered in ALS
Comment: oxidative stress modulates c-Ret function, thereby reducing GDNF signaling in motor neurons. induction of c-Ret expression in microglia may contribute to non-cell autonomous cell death of motor neurons by available GDNF in ALS.
Citation: Ryu, H., Jeon, G. S., Cashman, N. R., Kowall, N. W., & Lee, J. (2011). Differential expression of c-Ret in motor neurons versus non-neuronal cells is linked to the pathogenesis of ALS. Laboratory Investigation; a Journal of Technical Methods and Pathology, 91(3), 342–52. doi:10.1038/labinvest.2010.203
Back to Homepage